The deadlift is a staple of most strength-training programs, and it’s one of the three lifts performed in the sport of powerlifting.
Deadlifts can be performed using a variety of training tools, with the barbell being the most common option.
A large body of research supports the use of the deadlift for a variety of fitness and performance goals — both among athletes and the general population.
Multiple deadlift variations offer different but related benefits compared with the conventional deadlift. These variations allow the deadlift pattern to be incorporated into a fitness program tailored toward your needs.
This article discusses the benefits of deadlifts and offers a few deadlift variations to add variety and customization to your workouts.
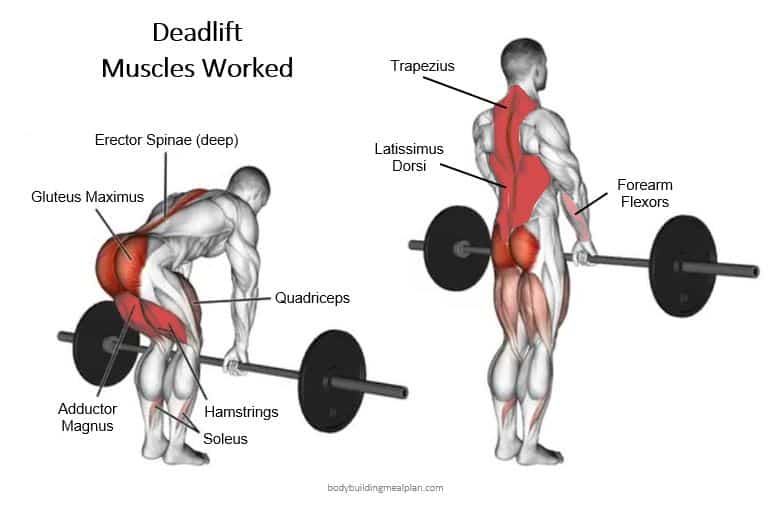
The deadlift is a widely used compound weight exercise that involves picking up a weight from the ground by bending at your waist and hips and standing back up.
The deadlift exercise and its variations require you to bend over while maintaining a braced, neutral spine, gripping the weight, and driving through the floor with your feet. The motion uses your glutes, hamstrings, and quadriceps to lift the barbell off of the floor.
In the standard deadlift, the initial level change to grasp the bar comes through a combination of hinging at the hips and bending your knees. In a standard deadlift, your torso angle at the beginning of the pull will be roughly 30–45 degrees above horizontal.
Throughout the motion, you must keep your core contracted to stabilize your spine and avoid any twisting, rounding, or arching throughout your torso.
All deadlift exercises begin with the weight roughly in line with the middle of your foot before bending forward and picking up the object.
Deadlifts are highly effective at increasing functional strength due to the activation of your largest lower body muscles.
They also train you for the functional activity of safely lifting objects off of the floor, which is a key skill for day-to-day activities.
The top 8 benefits of deadlifts
Here are 8 evidence-based benefits of incorporating deadlifts into your training program.
1. Activate your hip extensors
Deadlifts are among the best exercises for training your hip extensors. Your hip extensors include the gluteus maximus and hamstring complex, which are commonly targeted muscles in fitness programs due to their functional use and aesthetic appeal when properly trained.
Research suggests that deadlifts are superior to squats when it comes to training these muscles. Still, squats offer different benefits than deadlifts and are also an important component of well-rounded fitness programs .
The activation of the gluteus maximus and hamstrings when performing deadlifts will lead to both increased strength and size of these muscles.
2. Reduce lower back pain
Lower back pain is an incredibly common complaint among the general population.
While there are many causes of lower back pain that require differing treatments, research suggests that for mild mechanical low back pain, deadlifts can be an effective tool for reducing or reversing this ailment .
Note that proper deadlift technique with a braced, neutral spine is crucial for ensuring deadlifts do not aggravate your pain. You should consult a healthcare professional before attempting deadlifts as part of a treatment for lower back pain.
3. Improve jump performance
Jumping is a key skill for a variety of athletic and recreational activities, and your jumping ability often reflects the overall development of your lower body power.
Plus, the increased power reflected in the ability to jump transfers to other maximal power activities like sprinting.
Research suggests that deadlifts are among the most effective strength-training exercises for improving maximal jump performance.
4. Improve bone mineral density
Loss of bone mineral density is a common effect of aging and a major health issue facing older adults.
Advanced loss of bone mineral density results in osteoporosis, which greatly increases the risk of fractures among older adults. Fractures can lead to a cascade of ongoing physical health problems related to loss of mobility.
Fortunately, a large body of research supports the use of resistance training to slow or even reverse age-related loss of bone mineral density. This includes the use of exercises such as the deadlift .
The key to increased bone mineral density is performing weight-bearing exercises that load the whole body with external resistance.
The location of increased bone density is directly related to the area of the body being trained. Specifically, the area of the muscles that work to perform the given movement will experience the most improved bone mineral density.
Given that the deadlift targets your legs and hips, performing deadlifts in conjunction with other resistance exercises can be an effective way to reduce or reverse age-related loss in bone mineral density.
5. Activate your core
Training your trunk muscles and core is a key aspect of well-rounded fitness programs.
While many different exercises train your core, research has suggested that deadlifts and other free-weight exercises are an effective way to activate and strengthen the muscles that stabilize your spine, such as the external oblique, rectus abdominis, and erector spinae .
6. Boost your metabolism
Weight loss is a common goal of many fitness programs. Successfully losing weight, particularly via losing body fat, requires you to burn more calories than you consume in a given period of time.
Traditional weight loss programs combine dietary modifications to reduce calorie intake and physical activity to increase calorie burning.
When it comes to effectively increasing your metabolism through movement, studies suggest that resistance training with exercises like the deadlift may be among the most efficient methods to increase calorie burn, all with less overall time spent training in the gym.
Additionally, the muscle growth you’ll experience over time will help you burn more calories at rest throughout the day.
7. Carry less risk during failed repetitions
The previously mentioned benefits are based on scientific research. Yet, there are some subjective benefits of deadlifts that make them an effective exercise in practice.
For example, deadlifts allow you to lift large amounts of weight without positioning the weight on top of you. In the event of a failed repetition, you can usually safely drop the weight without risking major injury.
Exercises like the barbell back squat or bench press are also effective training methods. However, you generally cannot risk going as heavy without a spotter given that a failed repetition can literally crush you.
If you typically work out alone, deadlifts are a good way to safely add heavier training to your workouts.
8. Offer simplicity of equipment
The final subjective benefit of deadlifts is the relative simplicity of the equipment. All you need is a barbell and some plates, or a weighted object with a handle, such as a kettlebell, to perform the movement.
Unlike other exercises that require specific equipment or access to a power rack, deadlifts are a very minimalist exercise for the extensive benefits they provide.




0 Comments